Summary: in this tutorial, we will introduce you to the Books DB2 sample database for practicing with DB2 tutorials.
Introduction to Books DB2 sample database
The Books database is a simple sample database designed for learning and practicing DB2. It consists of six tables:
-
bookstable stores book data including title, total pages, rating, ISBN, and published date. -
publisherstable stores publisher names. -
authorstable stores books’ authors. -
book_authorstable stores the relationship between books and authors. A book can be written by one or more authors, and one author may have one or many books. -
genrestable stores book’s genres. Genres data is hierarchical which is specified by values in the parent_id column -
book_genrestable stores the relationship between books and genres. A book may belong to one or more genres and a genre may have one or many books.
The following database diagram illustrates the tables and their relationships:
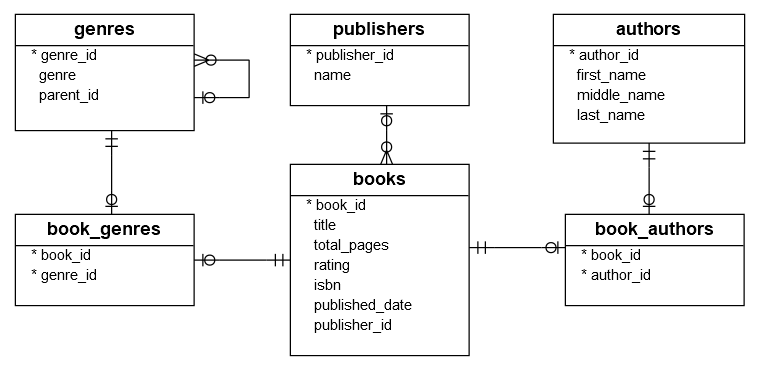
Database Tables
Table publishers
The publishers table has two columns that store publisher identification and name.
CREATE TABLE publishers(
publisher_id INT GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(publisher_id)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Table books
The books table has 7 columns that store book identification, title, total pages, ISBN, published date, and the identification of the publisher. Each book belongs to a publisher and a publisher may have one or many books. If the value in the publisher column is NULL, it means the publisher is unknown at the time of recording the book.
CREATE TABLE books(
book_id INT GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY NOT NULL,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
total_pages INT NULL,
rating DECIMAL(4, 2) NULL,
isbn VARCHAR(13) NULL,
published_date DATE NULL,
publisher_id INT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(book_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_publisher
FOREIGN KEY(publisher_id)
REFERENCES publishers(publisher_id)
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The following picture illustrates the relationship between books and publishers tables:

Table authors
The authors table has 4 columns that store author identification, first name, middle name, and last name.
CREATE TABLE authors(
author_id INT GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY NOT NULL,
first_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
middle_name VARCHAR(50) NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(100) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(author_id)
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Table book_authors
CREATE TABLE book_authors (
book_id INT NOT NULL,
author_id INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(book_id, author_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_book
FOREIGN KEY(book_id)
REFERENCES books(book_id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_author
FOREIGN KEY(author_id)
REFERENCES authors(author_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Each author has one or many books while each book is written by one or multiple authors. The relationship between books and authors is many to many as described in the following picture:

Table genres
The genres table has three columns that store genre identification, genre, and the relationship between genres.
CREATE TABLE genres (
genre_id INT GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY NOT NULL,
genre VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
parent_id INT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(genre_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_parent
FOREIGN KEY(parent_id) REFERENCES genres(genre_id)
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture shows the genres table:

Table book_genres
The book_genres table stores the relationship between books and genres by using two columns: book_id and genre_id.
CREATE TABLE book_genres(
book_id INT NOT NULL,
genre_id INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(book_id, genre_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_book
FOREIGN KEY(book_id)
REFERENCES books(book_id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_genre
FOREIGN KEY(genre_id)
REFERENCES genres(genre_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The relationship between books and genres are many-to-many:
In this tutorial, you have learned about the books DB2 sample database for practicing with DB2. In the next tutorial, you will learn how to create the Books sample database and load data into it.